If you want youthful skin, start with "Anti-Glycation"!
Do you feel like your appearance looks older than your actual age? It’s likely because you’ve started experiencing “Glycation”, which affects the condition of your skin.
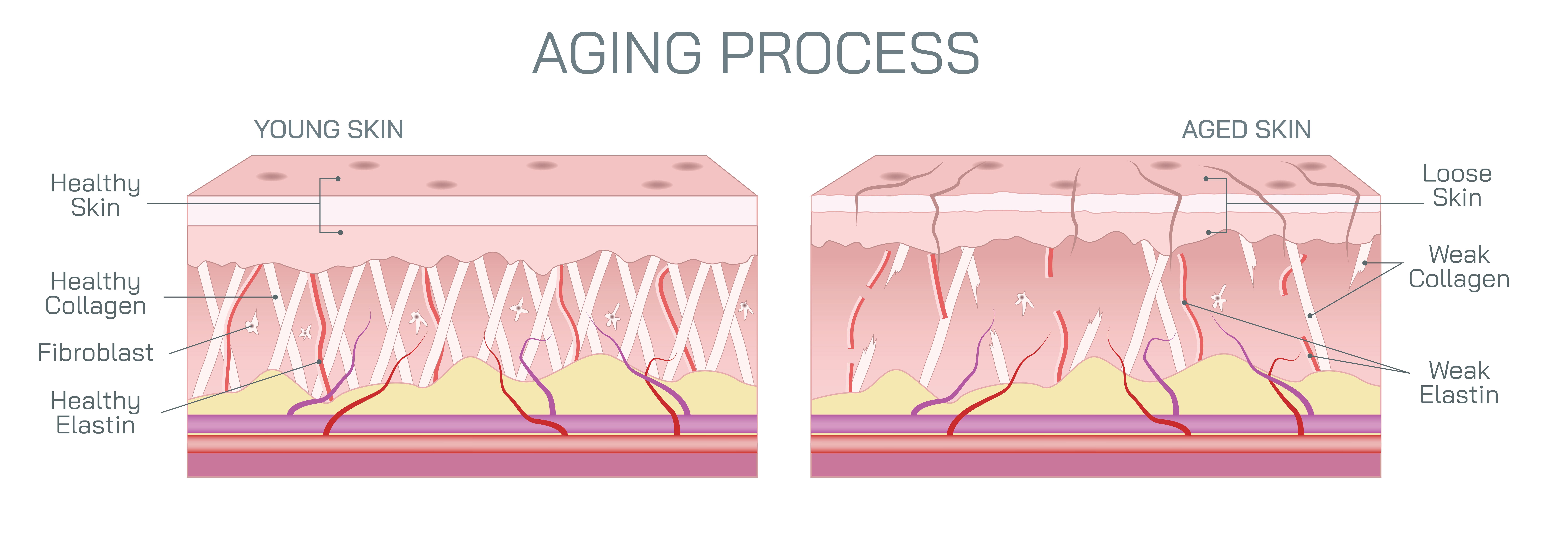
What is "Skin Glycation"?
Glycation occurs when excess sugar combines with proteins to form Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs), leading to hardened collagen, reduced elasticity, and signs of aging such as dullness, sagging, and wrinkles.
For example, think of the toast we eat. Freshly toasted bread is white, but if it continues to heat, it gradually turns deep brown or even black. This change is the result of a "glycation reaction." The burned part is the "Advanced Glycation End Products."
How to Combat Glycation?
Anti-glycation is very important because it helps protect the skin and delay aging. Starting anti-glycation early is like applying a “protective shield” to the skin. What are the ways to combat glycation?

1. Anti-Glycation Skincare
Choose skincare products with anti-glycation ingredients like carnosine, vitamin B1, and B6 to help combat skin dullness and sagging caused by glycation.
3. Healthy Lifestyle
Maintain a regular routine, exercise regularly, and ensure adequate sleep to promote sugar metabolism and support skin health.
2. Low Sugar Diet
Reduce the intake of high-sugar foods, especially desserts and sugary drinks, to minimize sugar’s damage to collagen through dietary adjustments.
4. Proper Sunscreen Protection
UV radiation can trigger oxidative stress in the skin, leading to the formation of AGEs and causing oxidative damage. Therefore, it is essential to protect your skin with sunscreen.
1. Wrinkles
When collagen in the skin undergoes glycation, its elasticity gradually weakens, causing the skin to appear loose and swollen.
2. Acne
Increased oil production and glycation could, in some cases, contribute to acne.
3. Dullness
The glycation reaction can affect the skin’s radiance, resulting in an uneven skin tone, dullness, or yellow spots.
4. Loss of Elasticity
When collagen and elastin undergo glycation, they become stiff, causing the skin to lose its softness and elasticity, resulting in a sagging appearance.
Benefits of Anti-Glycation
Reduce Acne: Regulating sugar intake balances hormone levels in the body, controls oil secretion, and prevents or reduces the occurrence of acne
Slower Aging: Controlling sugar consumption reduces insulin secretion, protecting collagen and elastin in the skin and slowing down the aging process
Disease Prevention: Reducing sugar intake helps regulate blood sugar levels, preventing diseases like diabetes and hypertension.
